
Table of Contents
Why Your Brain Loves Stillness
When you close your eyes, slow your breath, and drop into deep meditation, something remarkable happens. Beneath the calm surface, your brain is buzzing with activity — reorganising itself, calming overactive circuits, and even rewiring old patterns.
Meditation is no longer just a spiritual practice whispered about in monasteries. Today, neuroscientists map its effects in real time, using brain scans to watch what shifts when we quiet the mind. And the results? They’re astonishing.
We now know that deep meditation doesn’t just help you feel calmer — it can physically change your brain’s structure, balance its chemistry, and improve the way different regions communicate with each other. These changes can boost your focus, emotional resilience, and even slow down age-related decline.
In this article, we’ll explore exactly what happens to your brain during deep meditation, the regions that light up (and those that quiet down), and why these changes are linked to better focus, emotional balance, and overall wellbeing. Whether you meditate daily or have never tried it before, you’ll discover the science-backed reasons your brain may thank you for sitting still.
Related reading:
- Transform Any Room into a Zen Meditation Oasis – create a space that supports your mental clarity.
- 10 Must-Have Supplements to Turn Your Weak Immune System into a Powerhouse – because your brain and immune system are deeply connected.
The Science of Deep Meditation
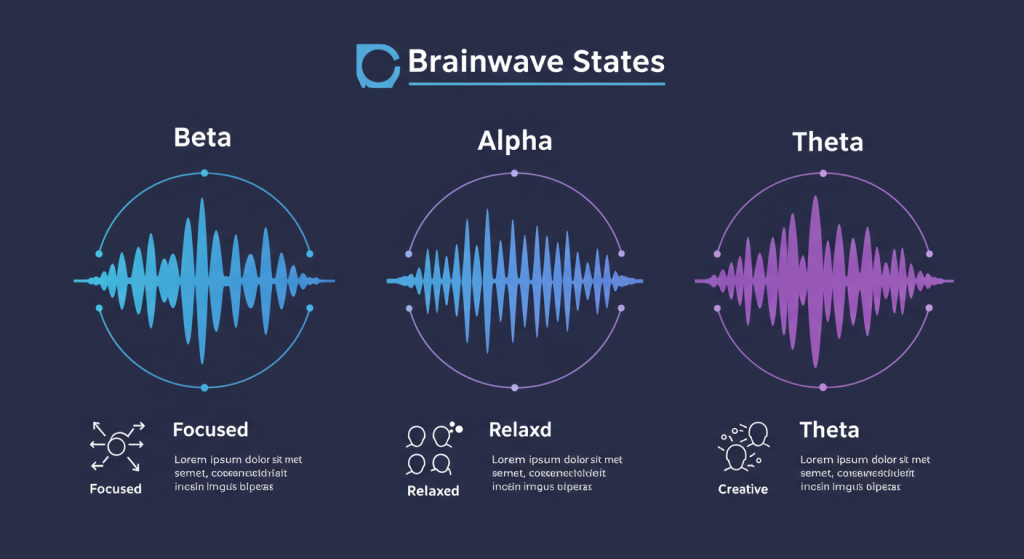
Meditation comes in many forms — mindfulness, transcendental, loving-kindness — but deep meditation shares one core feature: it moves you into a brainwave state far different from your everyday thinking.
When we’re awake and problem-solving, our brains run on beta waves — fast, busy, and often stressed. In deep meditation, beta activity slows, and alpha and theta waves become dominant. Alpha waves are linked to relaxed alertness, while theta waves are associated with deep relaxation, creativity, and subconscious processing.
Modern tools like fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and EEG (Electroencephalography) allow researchers to watch this shift in real time. They’ve found that even short, regular meditation sessions can physically change the brain — a phenomenon known as neuroplasticity, where the brain forms new connections and strengthens beneficial pathways.
One landmark study by Harvard researchers showed that just eight weeks of mindfulness meditation increased grey matter density in brain regions associated with memory, empathy, and emotional regulation.
The Default Mode Network — and Why It Matters
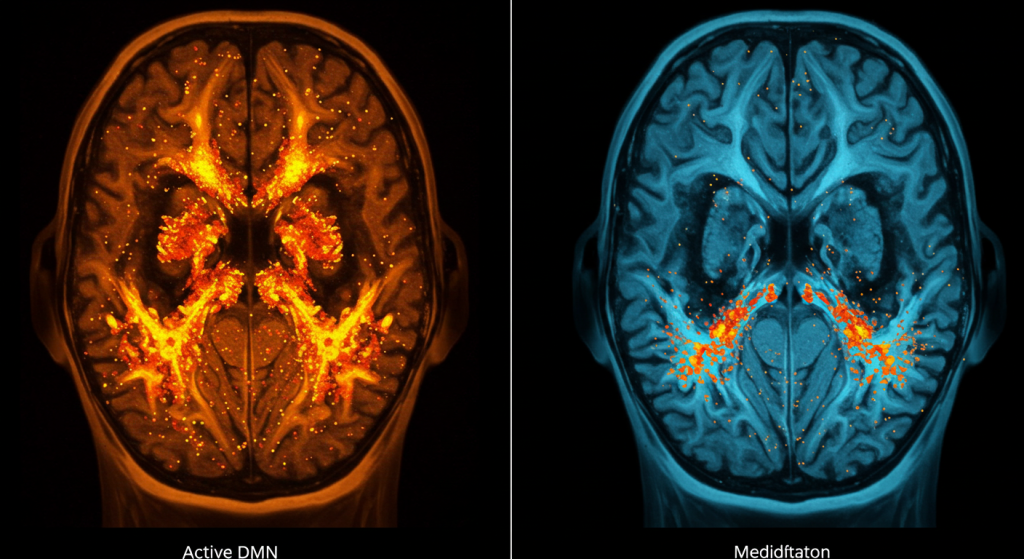
One of the most fascinating discoveries in meditation research is the role of the Default Mode Network (DMN). This network switches on when your mind wanders — thinking about the past, worrying about the future, replaying conversations. It’s also where overthinking and self-criticism thrive.
During deep meditation, DMN activity decreases. This quieting effect means fewer self-critical thoughts, less anxiety, and more present-moment awareness. In people with depression or chronic stress, the DMN is often overactive. Meditation helps balance this, allowing the brain to rest and reset.
Over time, a calmer DMN may even reshape your baseline mood — you don’t just feel better during meditation; you carry that balance into your daily life.
Related reading:
- Why Meditation is Essential for Busy Moms: Tips & Tools for Finding Time to Unwind – practical ways to fit mindfulness into a packed schedule.
Brain Regions That Change with Deep Meditation
Meditation isn’t just a mental exercise — it’s a full-brain workout. Here’s what science shows happens to specific regions:
1. Prefrontal Cortex — The Mind’s Control Centre
Handles planning, decision-making, and focus. Regular meditation can thicken the prefrontal cortex, boosting your ability to stay calm under pressure and make thoughtful decisions.
2. Amygdala — The Brain’s Alarm Bell
This almond-shaped structure triggers fear and stress responses. Meditation has been shown to reduce amygdala size and reactivity, making it easier to respond thoughtfully instead of reacting impulsively.
3. Hippocampus — Memory & Learning Hub
Responsible for forming new memories and learning, the hippocampus grows stronger with consistent meditation, improving recall and mental flexibility.
4. Insula — Your Interoception Centre
The insula helps you sense internal signals like your heartbeat and breath. A more active insula improves body awareness, emotional regulation, and self-care habits.
Neurochemicals Released During Meditation
Deep meditation isn’t just about “thinking less” — it triggers a powerful neurochemical shift in the brain that explains why you feel so good afterward.
When you meditate deeply, your brain moves into a more balanced state of neurotransmitter activity. This means the brain releases and regulates key chemicals that influence mood, focus, and resilience:
- Dopamine – The Motivation Molecule
- Meditation boosts dopamine levels, particularly during focused attention practices.
- Higher dopamine means more motivation to stick to healthy habits and a greater sense of reward after completing tasks.
- This is one reason people feel more optimistic and productive after meditating in the morning.
- Serotonin – The Mood Stabiliser
- Often called the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, serotonin helps regulate mood, appetite, and sleep.
- Meditation naturally elevates serotonin levels, which can help reduce symptoms of mild depression and anxiety.
- Unlike quick mood boosters (like sugar or caffeine), serotonin from meditation doesn’t cause a crash — it supports steady emotional balance.
- Endorphins – The Natural Pain Relievers
- These are your body’s natural opiates, reducing pain perception and producing a mild euphoric feeling.
- Endorphins explain why meditation can be a helpful companion for chronic pain management.
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) – The Calming Agent
- GABA is the brain’s main inhibitory neurotransmitter, which quiets overactive brain circuits.
- Increased GABA levels during meditation help reduce restlessness and racing thoughts.
The takeaway: Meditation creates a chemical “cocktail” that supports mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall well-being — without side effects. It’s like a natural mood stabiliser that works from the inside out.
Long-Term Brain Changes
The benefits of meditation extend far beyond the session itself. Over weeks, months, and years, the brain begins to rewire and restructure in ways that are visible on brain scans:
- Increased Grey Matter Density: Especially in the hippocampus (memory) and prefrontal cortex (focus and decision-making).
- Stronger Neural Pathways: Better communication between the rational “thinking brain” and emotional “feeling brain.”
- Reduced Cortical Thinning: Normally, the brain’s cortex thins with age, leading to slower processing. Meditation slows this decline, meaning your brain may function “younger” for longer.
Case Study Highlight:
A Harvard Medical School study found that people who meditated for 30 minutes a day over eight weeks had measurable increases in grey matter density in the hippocampus and reduced grey matter in the amygdala — a structural change associated with stress reduction.
This suggests meditation isn’t just “relaxing” — it’s actively reshaping the brain to handle stress, focus better, and stay mentally sharp well into later life.
How to Start Your Own Deep Meditation Practice
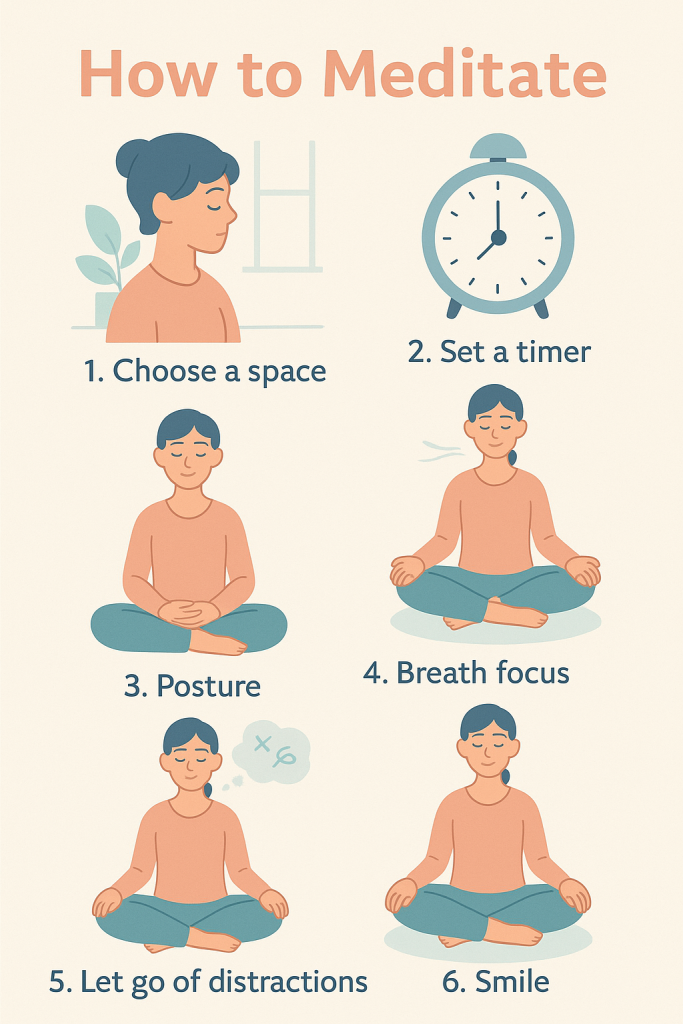
If you’ve never meditated before, the idea of “emptying your mind” can feel intimidating. The good news is — you don’t need to force anything. Deep meditation is more about observing without judgement than about stopping your thoughts entirely.
Step-by-Step Beginner Plan:
- Choose Your Space:
- Pick a quiet location with minimal distractions.
- For inspiration, read our Small Garden Design: 10 Inspiring Ideas — outdoor spaces can make wonderful meditation spots.
- Set a Timer:
- Start with 5–10 minutes. Increase slowly as your comfort grows.
- Adopt a Comfortable Posture:
- Sit cross-legged on a cushion or in a chair with feet flat on the floor. Keep your spine straight but not rigid.
- Focus on Your Breath:
- Notice the sensation of air entering and leaving your nose or the rise and fall of your chest.
- Handle Distractions Gently:
- When your mind wanders (it will), simply notice the thought without judgement and bring your attention back to your breath.
- Experiment with Guided Meditations:
- Apps like Insight Timer, Calm, or Headspace can help you explore different techniques.
Pro Tip: Consistency is more important than duration. Five minutes every day is more effective than 30 minutes once a week.
Conclusion
Deep meditation is more than a way to relax — it’s a proven method for strengthening your brain, balancing your emotions, and protecting your mental health over time. From calming the default mode network to reshaping key regions, the benefits go far beyond the cushion.
And the best part? Just a few minutes a day can start the transformation.
Related reading:
- Top 10 Books to Kickstart Your Holistic Health Journey
- Why Your Activewear Could Be Sabotaging Your Health
FAQ Sidebar
Q: How long does it take to see brain changes from meditation?
A: Some studies show results in as little as 8 weeks with daily practice.Q: Can deep meditation replace therapy?
A: It can complement therapy, but it’s not a replacement for professional care.Q: Is meditation safe for everyone?
A: Yes, but those with certain psychiatric conditions should consult a healthcare provider.Q: Morning or evening meditation — which is better?
A: Both work; consistency is more important than time of day.

I want assembling utile information , this post has got me even more info! .